
(GL – General Ledger Setup – Account Assignments)
General ledger posting throughout the system is controlled by the settings made in this screen.
Outside of this screen there is no exposure to GL accounts anywhere in the system except for the Supplier Invoices and Journal Entry screens. This gives the accounting department complete control over the general ledger and shields non-accounting personnel from any accounting setup or decisions.
Use the DBA standard chart of accounts
Use the standard chart of accounts supplied by DBA for your account assignment accounts and cross reference your Financial Accounting GL Account Numbers in the GL>GL Setup>Chart of Accounts>Detail tab X-Ref Account field. Most of the account numbers in the Account Assignments screen should be left intact and unchanged.
Special accounts to review
We recommend that you use the standard chart of accounts that is supplied with the system and adapt your existing accounts accordingly. If you do so, the only screens that potentially require entries are the following:
Sales Tab – Exceptions Sub-Tab
You may want to break your default Sales and COGS account combination into multiple Sales and COGS account combinations that correspond to Item Category or Customer Type.
Purchasing Tab – Exceptions Sub-Tab
You may want to break your default Misc Purchases account into multiple expense or asset accounts represented by individual descriptors.
Purchase Tax (Expense or Liability)
In the purchasing tab, you will have to choose whether you will treat your Purchase Tax as an expense or liability. Any tax entered in the PO Invoices screen is charged to this account. If you are subject to US-style taxation, this is normally an Expense account and applies primarily to not-for-resale purchases. If you are subject to GST-VAT style taxation, this is normally a Liability account.
Bank Accounts Tab
For companies using the DBA Legacy Financials, each bank account is given its own asset, interest income, and bank charges account.
Inventory Tab

Inventory (Asset)
In DBA all inventory (except for work in process) is represented by a single Inventory account.
Why one Inventory account?
In our experience, multiple inventory accounts (by location, item category, purchase or manufactured, finished or semi-finished, raw material or components, etc.) vastly complicate item setup and inventory account reconciliation and would be in conflict with our “alternative to over-complicated ERP systems” philosophy.
A single Inventory account is sufficient for balance sheet purposes. Detailed inventory value analysis is better achieved outside the GL via the Inventory Value report, which serves as a “sub-ledger” to your Inventory account. Instead of being limited to one valuation criteria, the Inventory Value report enables you to value current and past inventory value by item, location, item category, manufactured or purchased, and changes in values between two dates.
Because of the simplicity of the single Inventory account, a new stock item can be set up in DBA with only five required fields and without any accounting decisions to be made.
Inventory Adjustments or Adjustments COGs (Cost of Sales)
Transactions made in the Inventory Adjustments, Stock Counts, Change Inventory Cost, and Reconcile Book Value screens interact with this account.
Sales Tab
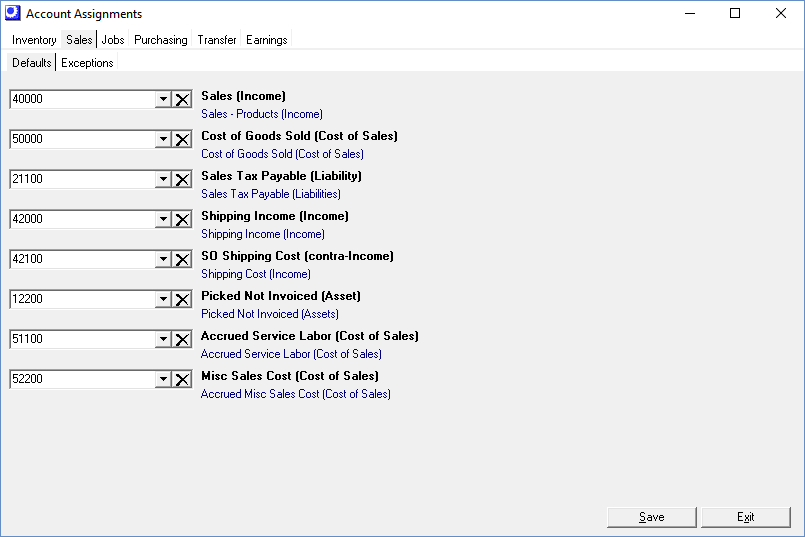
Defaults Sub-Tab
Sales (Income)
A default Sales account is required. In the Sales – Exceptions sub-tab you have the option of further breaking sales out by Item Categories or Customer Types.
Cost of Goods Sold (Cost of Sales)
A default Cost of Goods Sold account is required. In the Sales – Exceptions sub-tab you have the option of further breaking cost of goods sold out by Item Categories or Customer Types.
Sales Tax Payable (Liability)
The tax amounts on customer invoices are credited to this Liability account.
Shipping Income (Income)
Customer invoice shipping charges are credited to this Income account.
Shipping Cost (Income)
Freight bills pertaining to customer shipments are debited to this account. Even though it is a cost, it is usually classified as an Income account because it offsets the Shipping Income account and is usually located directly adjacent to it.
Picked Not Invoiced (Asset)
The Picked Not Invoiced account temporarily stores the cost of stock items that have been picked for shipment, but have not yet been invoiced. At time of invoicing, this account gets credited and Cost of Goods Sold gets debited. This is an Asset account, located in the chart of accounts following your Inventory account.
Accrued Service Labor (Cost of Sales)
When a sales order line is invoiced for a descriptor with a descriptor type of ‘LABOR’ or ‘SETUP’, this account is credited for the sales order line’s total estimated cost, with the corresponding debit made to Cost of Goods Sold. This is a Cost of Sales account, usually located in the chart of accounts following your Cost of Goods Sold account(s).
Misc Sales Cost (Cost of Sales)
When invoice costs are posted for any descriptors with a Descriptor Type of ‘MISC’ or ‘SUBCON’, this account is credited and the offsetting debit entry is made to Cost of Goods Sold or a COGS exception account. This is a Cost of Sales account, usually located in the chart of accounts following your Cost of Goods Sold account(s).
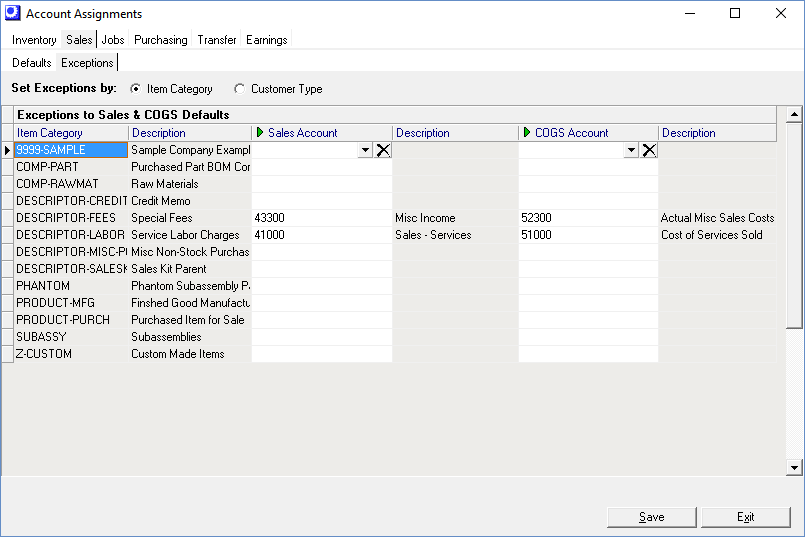
Exceptions Sub-Tab
Training Videos
Entries on this screen are optional. If you don’t make any entries, all sales will be posted to your default Sales and Cost of Good Sold accounts on the Sales – Defaults tab.
Set Exceptions by
Select Item Category if you wish to break your sales out by item categories. You can define item category exceptions against both Items and Descriptors.
NOTE: Most manufacturing companies are item-centric and define their Sales/COGs exceptions by Item Category.
Select Customer Type if you prefer to break out sales by type of customer.
▪All sales, including shipping income, will follow the Customer Type exception.
Exceptions to Sales & COGS Defaults (Grid)
| • | If Item Category is selected, all your Item Categories are listed in the grid. You can optionally assign each category to a Sales Account and/or a COGS Account. |
| • | If Customer Type is selected, all your Customer Types are listed in the grid. You can optionally assign each type to a Sales Account and/or a COGS Account. |
Jobs Tab
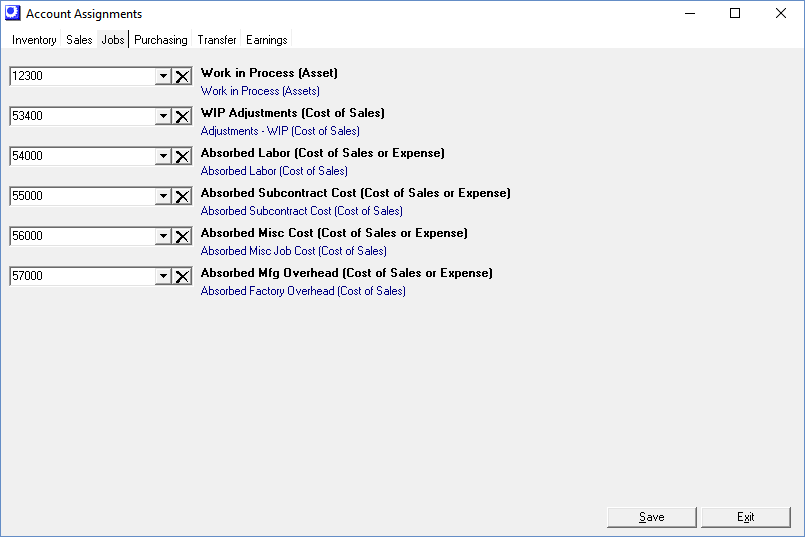
Work in Process (Asset)
This account represents the accumulated input costs (labor, setup, material, overhead, subcontract services, miscellaneous expenses) in your make jobs, less the output cost of finished item receipts. This is an Asset account and is located in the chart of accounts immediately following your Inventory account(s).
WIP Adjustments (Cost of Sales)
This account is used to bring the net Work in Process amount for each finished job to zero. When the job’s Status is changed to ‘CLOSED’, the program compares total incoming job costs with the total outgoing cost of job receipts. If a difference is found, the Work in Process account is adjusted up or down and the offset amount posted to this account. This is a Cost of Sales account, usually located in the chart of accounts following your Inventory Adjustments account.
Absorbed Labor (Cost of Sales)
This account represents the labor reported or issued to jobs. Locate this account adjacent to your Direct Labor payroll account and give it the same account type (Cost of Sales). The two accounts offset each other and are a “wash” on your books (although some variance is normal and expected).
Absorbed Subcontract Cost (Cost of Sales)
This is a clearing account for the subcontract services that are purchased and issued to jobs. Locate this account following your Absorbed Labor and Direct Labor accounts and give it the same account type (Cost of Sales).
Absorbed Misc Cost (Cost of Sales)
This is a clearing account for miscellaneous costs (fees, special packaging, etc.) that are purchased and issued to jobs. Locate this account following your Absorbed Subcontract Cost account and give it the same account type (Cost of Sales).
Absorbed Mfg Overhead (Cost of Sales)
This account represents the manufacturing overhead burden applied to jobs. Locate this account following your Absorbed Misc Cost account and give it the same account type (Cost of Sales).
Purchasing Tab

Defaults Sub-Tab
Misc Purchases (Expense)
DBA requires a default Misc Purchases account that is a “catch all” account for all non-inventory, non-job related purchases. You can optionally break out your miscellaneous purchases by descriptor on the Purchasing – Exceptions sub-tab.
Received Not Invoiced (Liability)
This account temporarily stores the credit offset entry that is made when PO lines are received. When the PO invoice line is matched for this line, this account gets debited and Accounts Payable or PO Invoice Transfer is credited. This is a Liability account, located following your Accounts Payable account.
RNI Adjustments (Cost of Sales)
When a PO line is closed, any difference between total receipt costs and total invoice costs is posted to this account. Most likely your outside system does not have such an account. This is a Cost of Sales account, located following your WIP Adjustments account.
PO Shipping Cost (Cost of Sales)
Shipping charges entered in the PO Invoices screen are debited to this account. This is a Cost of Sales account and is located following your Misc Sales Cost account.
Purchase Tax (Expense or Liability)
Any tax entered in the PO Invoices screen is charged to this account. If you are subject to US-style taxation, this is normally an Expense account and applies primarily to not-for-resale purchases. If you are subject to GST-VAT style taxation, this is normally a Liability account.
Exceptions Sub-Tab
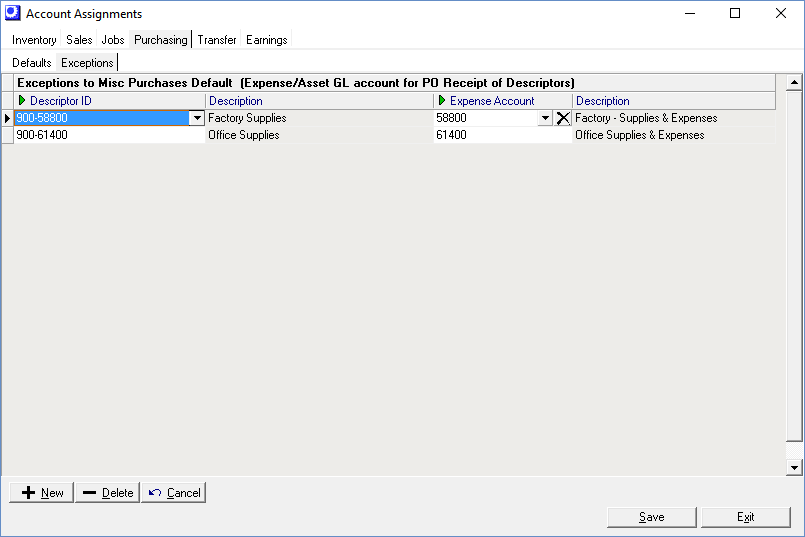
Misc Purchases Exceptions (Expense)
You can assign specific descriptors to specific Expense (or Asset) accounts in this screen to handle the posting of non-inventory, non-job purchases. Whatever assignments you make in this screen override your default Misc Purchases account.
Non-Manufacturing Purchasing
In the non-manufacturing side of your business, you may want to assign purchases to individual departments such as sales, engineering, order entry, etc. To do this we suggest that you create separate sets of descriptors for each department and assign each descriptor to its appropriate expense or asset account. Each department would then create POs using its own descriptors.
NOTE: If your purchasing people think in terms of GL accounts when buying miscellaneous items, consider using the GL account code as the Descriptor ID itself. Another approach is to incorporate the account code into the descriptor’s Description, which can be typed over during PO entry to describe the particular item being purchased.
Transfer Tab

This tab is only visible when the Financial Transfer option is selected in the Accounting Configuration screen.
AR Invoice Transfer (Asset)
The AR Invoice Transfer account is a clearing account used for the Financial Transfer Accounting Configuration (Transfer > AR Voucher Transfer).
AR Voucher Transfer process in outside accounting program
•Create an invoice for the special non-stock item/non-tax item that you created in your outside accounting system as part of the financial transfer setup. Do not attempt to include a tax code or tax detail in your financial accounting system.
•The non-stock item will be setup to credit the AR Invoice Transfer (Asset - 11150) account instead of a Sales account. The invoice debit will use your existing Accounts Receivable account.
•The debit values to the 11150 AR Invoice Transfer created during the DBA invoice process will be posted to the outside accounting system as part of the Transfer > GL Summary Transfer.
•The net effect is that the debit to the AR Invoice Transfer from the DBA invoice process will offset the credit for the AR Invoice Transfer voucher in your outside accounting system, thus leaving Accounts Receivable in your outside system for normal payment collection.
Line Item Sale - special non-stock item in outside system
Debit |
Accounts Receivable in outside system |
Credit |
AR Invoice Transfer (Asset - 11150) |
PO Invoice Transfer (Liability)
The PO Invoice Transfer account is a clearing account used for the Financial Transfer Accounting Configuration (Transfer > AP Voucher Transfer).
AP Voucher Transfer process (supplier bill) in outside accounting program
•Create a supplier bill to the AR Invoice Transfer account in your outside system. Do not attempt to enter a tax code or tax detail in your financial accounting system.
•The DBA credit values (AP Invoice Transfer - 20300) from the PO Invoice process in DBA will be posted to the outside system as part of the Transfer > GL Summary Transfer.
•The net effect is that the credit to the AP Invoice Transfer from the DBA PO Invoice process will offset the debit to the AP Invoice Transfer supplier bill entry in your outside accounting system, thus leaving Accounts Payable in your outside system for normal payment processing.
Supplier Bill - created in outside accounting
Debit |
AP Invoice Transfer (Liability -20300) |
Credit |
Accounts Payable in outside system |
AR Tab (Legacy Financials)
This tab is only visible when the DBA Legacy Financials option is selected in the Accounting Configuration screen.

Accounts Receivable (Asset)
This account represents the unpaid portion of customer invoices, exclusive of those written off to bad debt. Invoiced sales and shipping amounts are debits to this account and customer payments are credit entries.
AR – Tax Portion (Asset)
If in your country it is necessary to separately track the sales tax portion of total accounts receivable, you can designate a separate GL account in this field. If you do not need this, enter your Accounts Receivable account (see previous) in this field. Locate this account following your Accounts Receivable account.
AR Discounts Taken (Income)
If the customer takes a discount for early payment, the amount of the discount is debited to this Income account.
Customer Deposits (Liability)
Advance payments from customers for jobs are credited to this Liability account.
AP Tab (Legacy Financials)
This tab is only visible when the DBA Legacy Financials option is selected in the Accounting Configuration screen.

Accounts Payable (Liability)
This account represents the unpaid portion of supplier invoices. Supplier invoice amounts are debits to this account and supplier payments are credit entries.
AP – Tax Portion (Liability)
If in your country it is necessary to separately track the purchase tax portion of total accounts payable, you can designate a separate GL account in this field. If you do not need this, select your Accounts Payable account (see previous) in this field. Locate this account following your Accounts Payable account.
AP Discounts Taken (Cost of Sales)
If you take a discount for early payment of a supplier invoice, the amount of the discount is credited to this Cost of Sales account.
Banking Tab (Legacy Financials)
This tab is only visible when the ‘DBA Legacy Financials’ option is selected in the Accounting Configuration screen.

Bank Accounts
‘Bank Account’ type banking accounts are listed in this grid.
Banking Account
All your ‘Bank Account’ type banking accounts are listed in this column.
Asset Account
This is the Asset account associated with this bank account.
Interest Income
In the Account Reconciliation screen, interest income from bank statements is posted to this Income account.
Bank Charges
In the Account Reconciliation screen, bank charges from bank statements are posted to this Expense account.
Merchant Fees (optional)
In the Account Reconciliation screen, bank statement charges associated with merchant account fees (for customer credit card payments) is posted to this Cost of Sales account.
Merchant Accounts
‘Merchant’ type banking accounts are listed in this grid.
Banking Account
All your ‘Merchant’ type banking accounts are listed in this column.
Asset Account
This is the Asset account associated with this merchant account.
Merchant Fees
Transaction fees associated with customer credit card payment transfers made in the Merchant Account Transfer screen are posted to this Cost of Sales account.
Credit Card Accounts
‘Credit Card’ type banking accounts are listed in this grid.
Liability Account
This is the Liability account associated with this credit card account.
Credit Card Fees
In the Account Reconciliation screen, credit card fees and interest charges are posted to this Expense account.
Earnings Tab

Current Earnings (Equity)
Whenever you run a balance sheet, this account’s value is calculated (not stored) for the year to date.
Retained Earnings (Equity)
Whenever you run a balance sheet, this account’s value is calculated (not stored) and represents accumulated earnings outside of the current fiscal year.

