
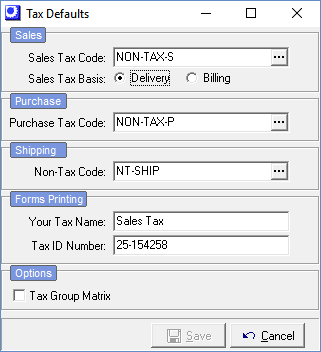
(Tax – Tax Defaults)
Use this screen to establish your system-wide defaults for sales and purchase taxation.
Link:
Screen Details
Sales
Sales Tax Code
This is the default tax code that is assigned to sales orders unless a tax code Exception is specified against the customer record.
United States
Select a default sales tax code that applies to the majority of your customers. For example, if most of your customers are in your local tax jurisdiction and are taxable, you would use your local tax code as the default. On the other hand, if most of your customers are out of state and are non-taxable, you would create a non-taxable, out of state tax code and use it as the default.
International
Typically, the default sales tax code is your VAT or GST tax that applies to most, if not all, your sales.
Sales Tax Basis
Against each customer record, you can optionally select a tax code Exception that gets assigned to the sales order header instead of the default sales tax code. You have two options for designating tax code exception(s) against the customer record:
Delivery
Select this option if you want the ability to designate a tax code exception against customer delivery addresses in addition to assigning a tax code exception against the main address. This enables the shipment destination to determine the tax code that gets applied to the sales order, which is how taxation authority is determined in the United States.
Billing
Select this option if you only want the ability to assign a tax code exception against the main address and not against delivery addresses.
Purchase
Purchase Tax Code
This is the tax code that is assigned to purchase orders and supplier invoices unless a tax code Exception is specified against the supplier record.
United States
Select a default purchase tax code that applies to the majority of your purchases and supplier invoices. For most manufacturers, this will be a non-taxable tax code because most purchases for resale are exempt from tax.
International
Typically, the default purchase tax code is your VAT or GST tax that applies to most, if not all, your purchases.
Shipping
Taxation on shipping is controlled at the Tax Code level (Taxes > Tax Codes). If Tax Shipping is checked, when shipping lines are created by adding a descriptor (Type = SHIP), the line tax code will use the SO or PO header tax code. If shipping charges are added at the time of sales shipment generation or during PO Invoice matching, the freeform line will use the SO or PO header tax code.
Non-Tax Code
If the header tax code for a Sales Order or Purchase Order uses a Tax Code that does not explicitly tax shipping, this default non tax code will be used. This default tax code is assigned to descriptors (Type = SHIP) that are added to sales order and purchase order details, or to freeform lines that get created when non-taxable shipping charges are entered during sales shipment generation or PO Invoice matching.
NOTE: You must select a non-taxable tax code.
Forms Printing
Your Tax Name
Enter the name you want printed in the footer area of quotes, acknowledgments, invoices, and purchase orders as a description against the tax amount. Typical names would be ‘Sales Tax’, ‘GST’, ‘VAT’, etc.
Tax ID Number
This is your tax ID number. It currently has no formal use, but is available in the data pipeline on certain forms if you need it to print on the form.
Options
Tax Group Matrix
Select this checkbox if you want the option of assigning a Tax Group to customers, suppliers, items, and descriptors. In the Tax Group Matrix screen, you can assign tax codes against combinations of a customer/supplier tax group with an item/descriptor tax group.
How It Works
When entering sales orders and purchase orders, if a tax group is designated against the customer or supplier and it is matched against a tax group assigned to the item or descriptor, the tax code defined against that combination of tax groups in the Tax Group Matrix screen gets assigned to the line item as an exception to the header tax code.
Tax group combinations are used to designate tax code exceptions that are based on origin or destination and/or type of product or service. For example, a particular item might be subject to an excise tax or local tax that only applies to certain jurisdictions or country destinations. Using different combinations of tax groups, you can apply the special tax to some customers and not to others.

